Microscopic Approach for the Aging of Acoustical Materials
Microscopic approach for predicting acoustical properties of material
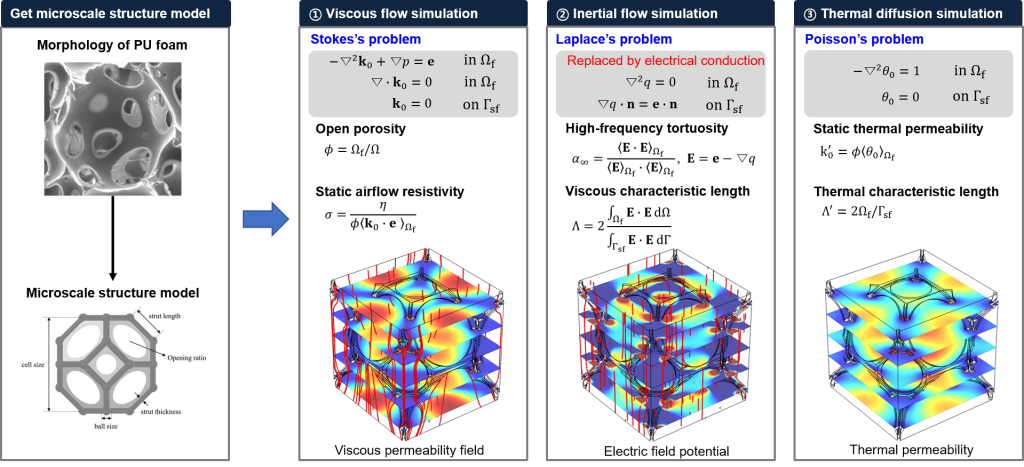
The sound absorbing material absorbs sound by converting sound energy into thermal energy by friction and kinetic energy of the material by the porous structure inside. Therefore, when the internal structure of the material is changed, the sound absorbing performance of the sound absorbing material is also affected. Flexible PU foam, one of the sound absorbing materials, have the open cell type morphology. At this time, the morphology composed of open cells can be modeled as a single microscale structure model. The structural characteristics of the material can be predicted through the flow and thermal simulation of the microstructure of the corresponding model. And then, Sound absorption performance of the material can be predicted using the predicted structural characteristics by microscale simulation and mechanical properties of the material.
Process for getting structural proterties from microscale morphology of material
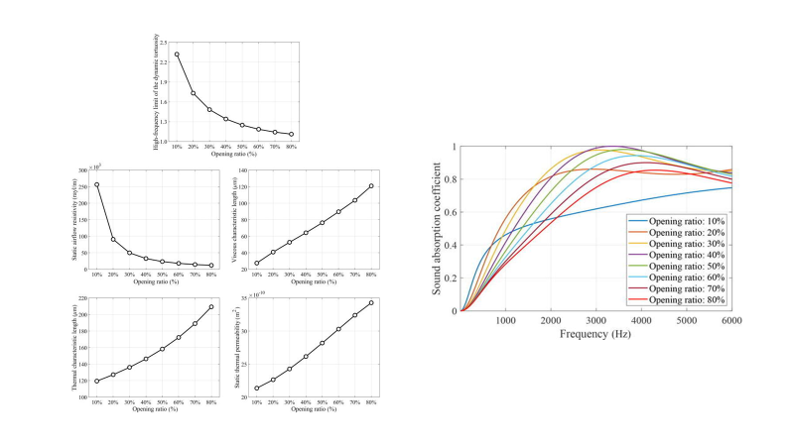
Parametric study of structural and acoustical properties by changing cell opening ratio
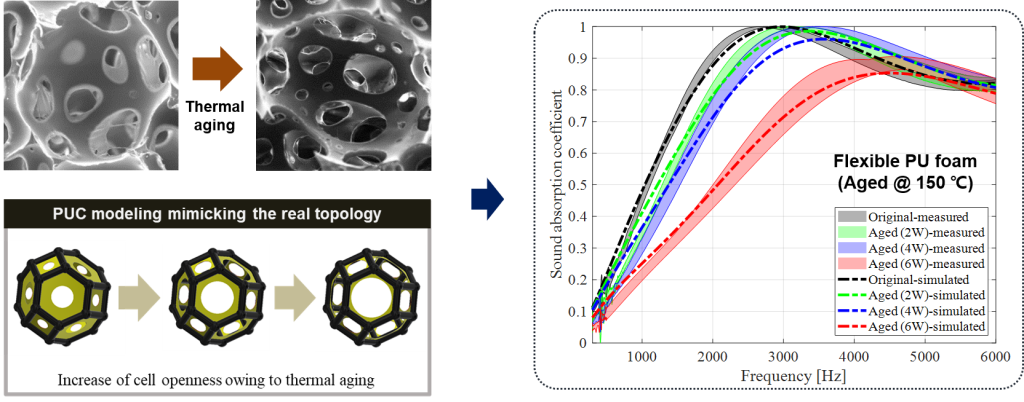
Application of microscopic approach : thermal ageing of acoustical materials
When PU foam, one of the sound absorbing materials, is exposed to a high temperature environment, the membrane covering the pores is destroyed and the morphology of the material is changed. And the phenomenon of membrane destruction in PU foam can be expressed as a microscale structure model with increased cell opening ratio. As a result of predicting the sound absorption coefficient by reflecting the change in cell opening to the microstructure model, it is confirmed that the aging sound absorption performance of the PU foam was well predicted.