Hybrid CAE/CAT
Complex machines such as automobiles have been modularized. That is, it is manufactured by combining existing parts with newly designed parts. In this case, dynamic characteristics of the combined product are predicted through Dynamic Substructuring (DS). This requires frequency response functions (FRF) at the exact interface to which each component is coupled. Using the experimental models makes it difficult to measure at the exact interface and requires lots of man hour. On the other hand, when using the numerical model, FRFs at the exact interface can be easily obtained, but a correlation process with experimental data is required. System Equivalent Model Mixing (SEMM) is introduced to overcome the limitations of each model and utilize the advantages.
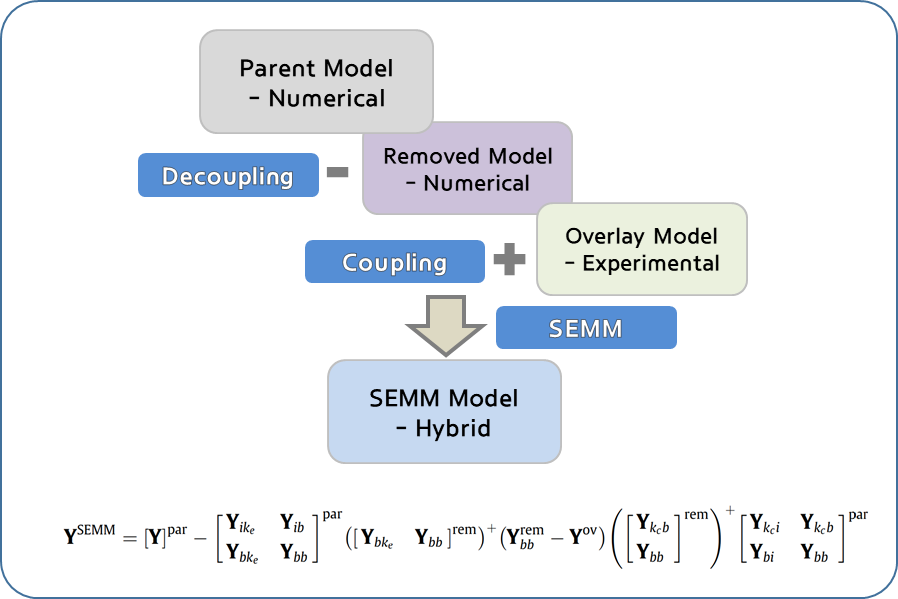
System Equivalent Model Mixing
SEMM is a process of mixing of the numerical model and the experimental model which are equivalent. The basics of SEMM is the FBS coupling of two models which considers the common DoFs of two models as an interface. Considering the numerical model as a parent model, the common DoFs are removed from the numerical model and coupled in the experimental model. As a result, the following equation is derived, and the inverse process of the experimental model matrix is not required, so it has the advantage of not being sensitive to test errors.